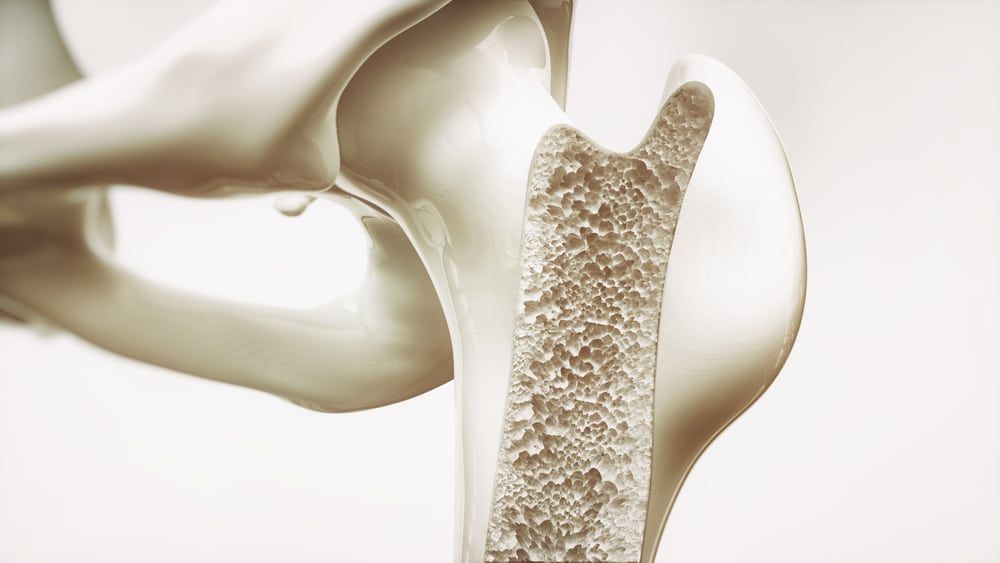
Osteoporosis is a condition in which bone mass deteriorates faster than the body can create new bone mass, causing the bones to become weak and fragile. Because of this, fractures are a common result of osteoporosis. This condition is most common among the older population; postmenopausal women in particular are highest at risk to develop the condition.
Did you know…
Hormone levels are an indication of susceptibility of Osteoporosis. When Estrogen levels have lowered, women’s bones grow weaker. Additionally, an overproduction of thyroid hormones can also promote bone mass loss.
A diet that is deficient in calcium will increase the likelihood of losing bone mass since calcium is essential to maintaining healthy bones. Another risk factor is a history of eating disorders. Generally, eating disorders result in decreased bone mass due to a decrease in body weight. Next, frequent consumption of alcohol is associated with osteoporosis. Smoking tobacco is another risk factor of the condition.
Maintaining a healthy diet, one with adequate amounts of protein, is a great way to keep bones strong. Some sources of healthy protein include soy, nuts, or legumes. A diet high in calcium is also best to prevent osteoporosis; calcium can be obtained from dark, leafy greens as well as fortified foods like cereals. Lastly, exercise can strengthen bones; it is important to create a routine with exercises you feel comfortable doing long-term.
The earliest signs are often receding gums, weakened nails, and an inability to grasp items firmly. Some symptoms that develop later are decreased height, a curved back posture, and vertebrae pain.